
NT-Center of Topographic
Historical introduction
The Topographic Survey Center (NT) of LECM integrated in the Coordination and Assistance Department (CA) develops its activities in the areas of positioning infrastructure and tridimensional modeling. In the first area, NT designs, installs, observes and calculates networks for the setting up of major engineering works and monitoring structures. For this purpose, LECM instituted at its foundation a sector featuring traditional positioning systems: tacheometry and leveling. In the early 90s, LECM was equipped with CAE (Computer Assisted Engineering) technology and at the end of that decade with GIS (Geographic Information Systems) technology. In the XXI century, LECM acquired a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) antenna, currently processing signals constellations GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and COMPASS. In 2011, NT has acquired a static terrestrial laser scanning system. In 2013, a second GNSS antenna and a second total station were purchased.
Being part of CA department, NT activity is transversal to LECM, keeping a close collaboration with other departments namely Department of Buildings and Structures (DEE) as well as with the Geotechnical Department (DG) in addition to direct collaboration with external clients.
Resources
Almost half of the human resources of NT have a university degree necessary for the operation of electronically supported acquisition systems and data logging as well as online processing of such data. Being in existence for 25 years, LECM has 7 sensors (two total stations, two levels, two GNSS antennas and a laser scanner) as well as 7 different software packages to process the information collected.
Existing human resources and equipment as well as the acquired experience allows NT regarding the future in terms of expanding to new applications like reverse engineering and compilation of heritage documentation as well as the utilization of new types of data acquisition systems, namely Mobile Terrestrial Laser Scanners which integrate GNSS technology and an Inertial Measuring Unit (IMU).
Precision Levelling with LEICA DNA03 & LS15 Settlement of Ground /Structures /Building Measurement
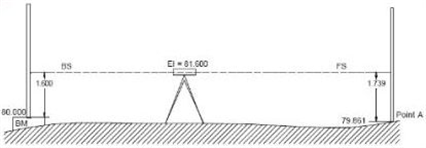
Digital Level -Leica DNA03 and LS15 is impeccable as it measures/determines the height and distance to the staff (level monitoring point) at the press of a button and calculates the height of the points. No readings are required and there is no copying or writing down and no calculations by hand.
The measurements are free from the earth’s curvature. Above all with invar staffs, can provide accuracy of 0.3mm/at 1km double run-ISO17123-2
A digital level is set on a tripod and reads a bar coded staff using electronic laser. The height of the staff where the level beam crosses the staff is shown on a digital display.
The digital precise level makes the survey process easier. The interpolation of the graduation is not made by the observer, but is made in an automated manner, eliminating all field procedure errors from the operator and increases the accuracy.

Benchmarks for datum and level monitoring points are located/installed after careful study of the area or structure to be measured

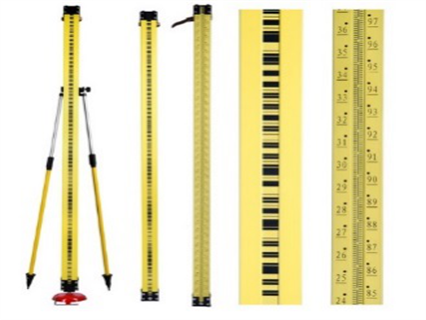
Digital level Leica DNA03 instrument together with invar staff with graduated scales, equipped with rod bubbles are used with special holders for steadiness. The digital level reads the bar code staff using electronic laser method from the back side and the front side, which gives the difference in the height. After auto processing the precise height, the level is calculated. The recommended distance from the instrument to the level monitoring point is less than 50m. When surveying roads, bridges, airfields, the level survey measurement is stopped if the vibration is heavy, as this leads to error in the level measurement.

Invar or precise level rod made of special alloy -Nickel and steel to with low co-efficient of thermal expansion and equipped with rod bubble is used to eliminate error and facilitate and ensure verticality.

The measured height/level is displayed in the LCD of the instrument and recorded in is internal memory and additionally on a memory card, which is downloaded to the PC.
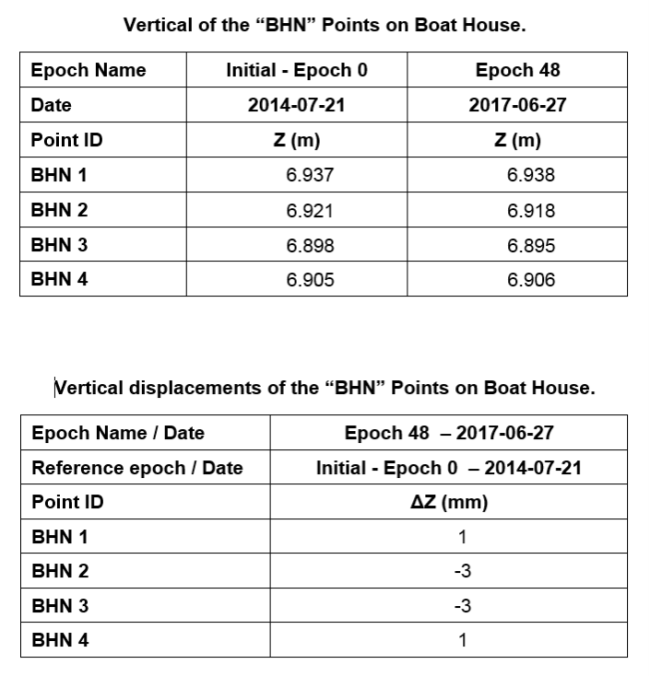
The data are processed and compared and presented in a report.
The results show the height in different epoch and the displacement in mm.
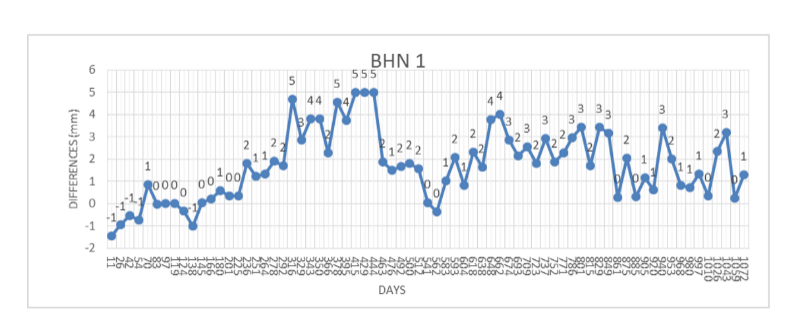
Graphical representation of the vertical displacement presented in the report
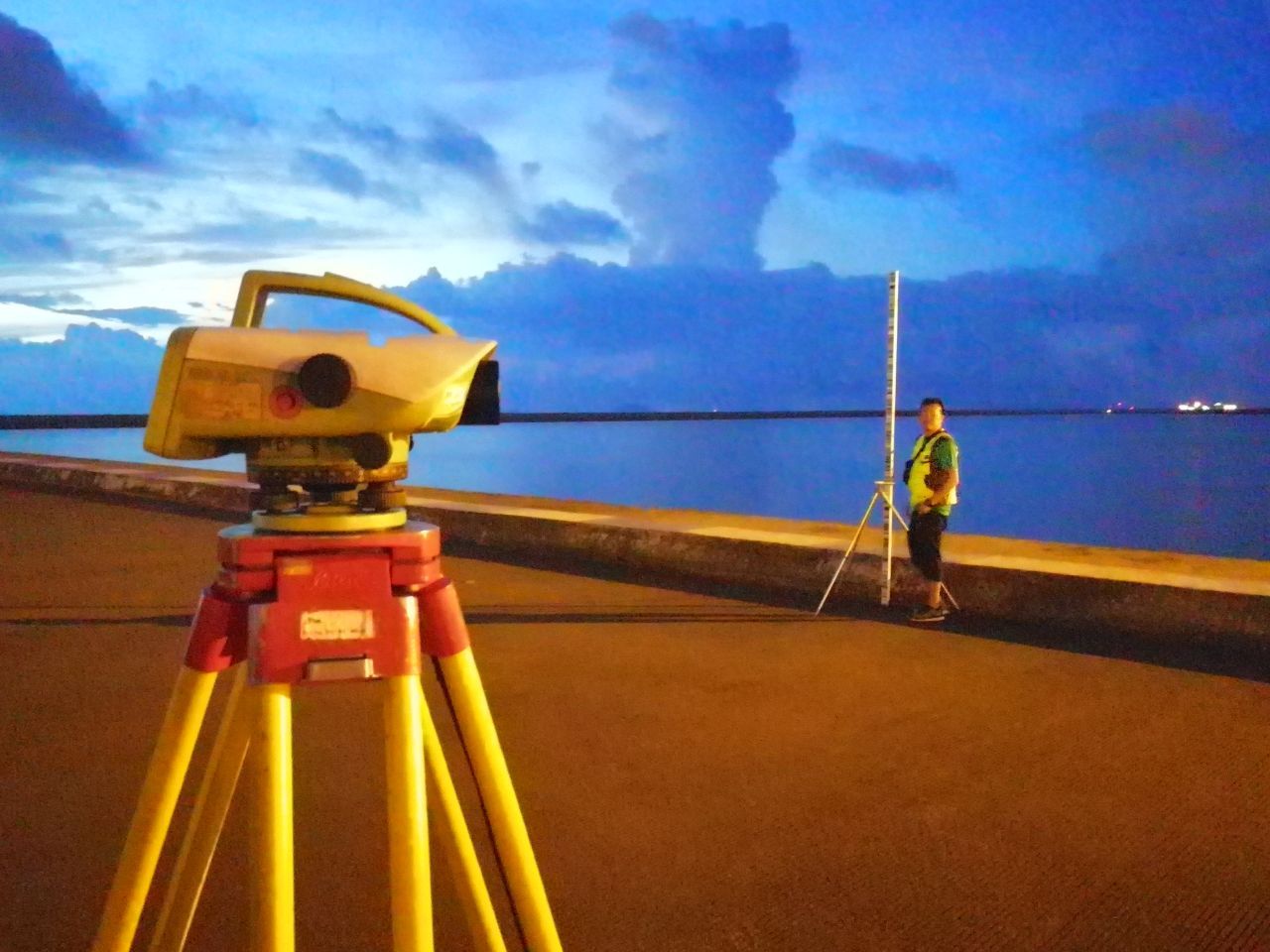

Macau International Airport - South Taxiway
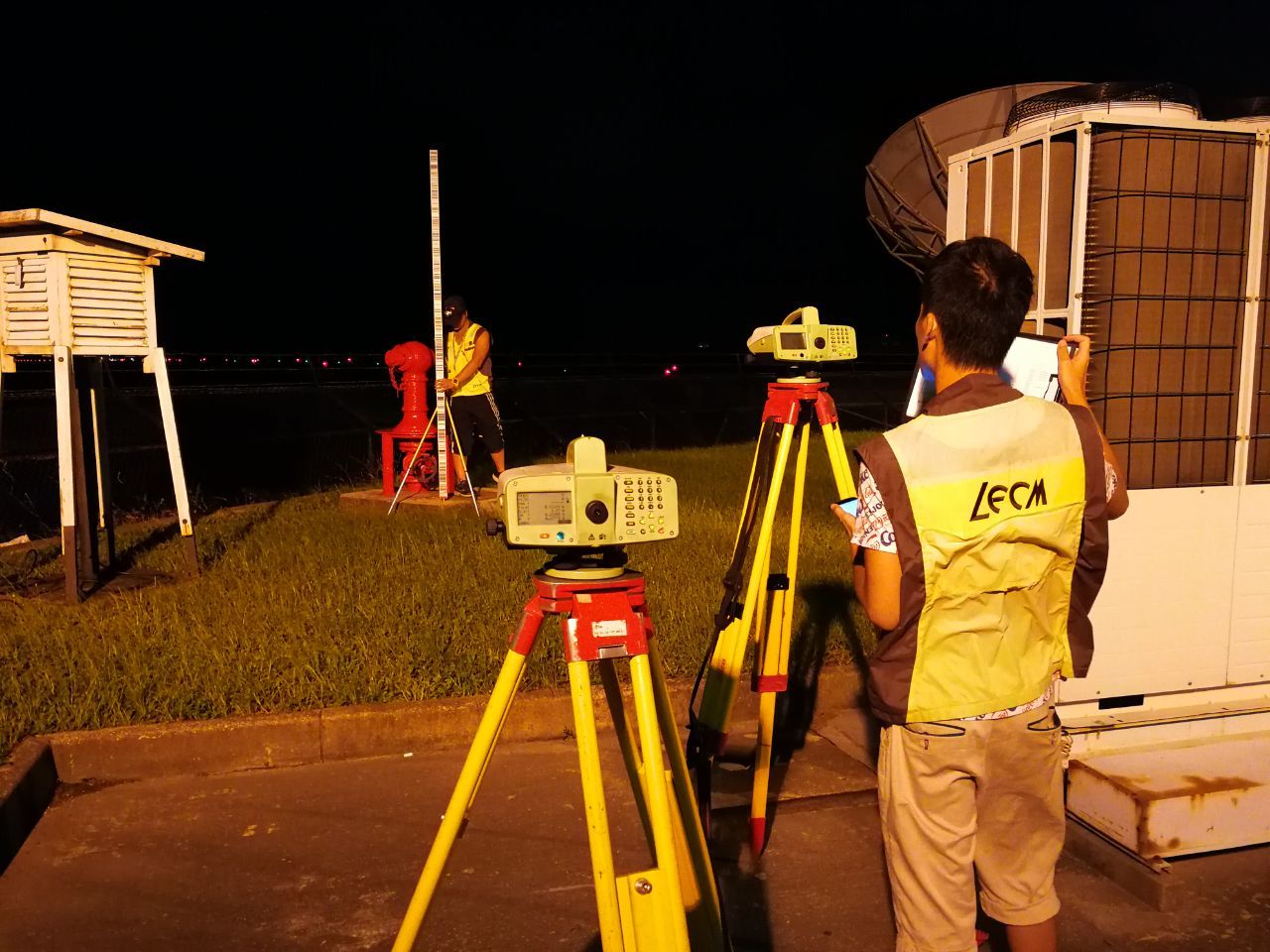

Macau International Airport Ground
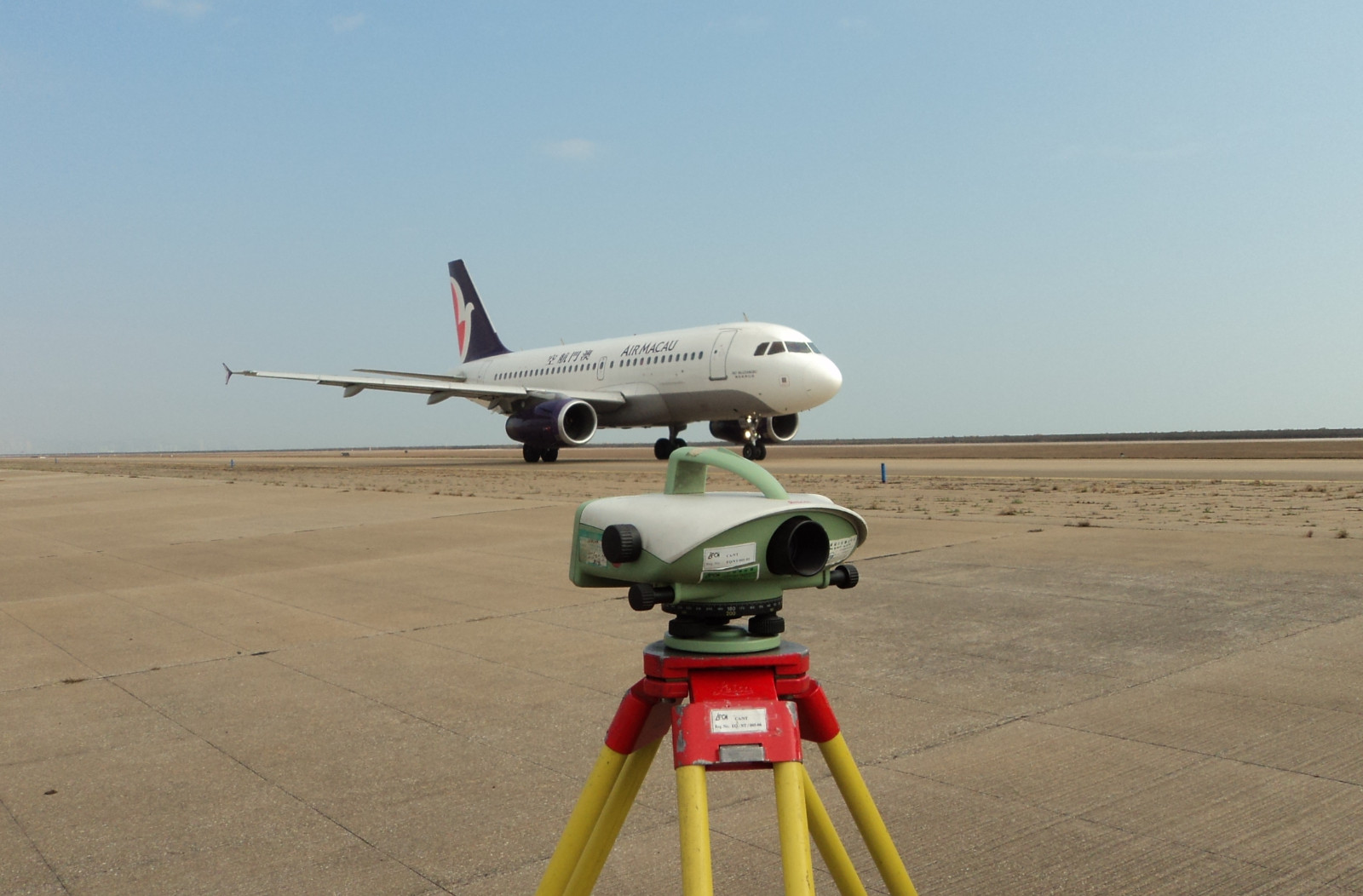

Macau International Airport - Runway
Surveying with Total Station Leica TM30 Measurement of Coordinates for Ground /Structures /Building
The total Station is used to measure the horizontal and vertical angles and distance to calculate the coordinates with fixed reference stations, where the target monitoring point must be in line of sight with the Total Station. It can provide millimeter accuracy: It combines accurate 0.5’ for angular measurement and millimetric precision for distance measurement, together with fast data acquisition.
TM 30 Total station is put in service specifically for monitoring application as it is reliable, incorporates excellent accuracy and can effectively and cost efficiently measure and control the health of vital structures. Monitoring with total Station requires the points to be stable, durable and reliable. Appropriate prism types are adopted for optimum accuracy. The limitations encountered with TM30 is mainly poor weather conditions, vibrations, etc. Apart from the equipment, the reference points are susceptible to settlement and damages.
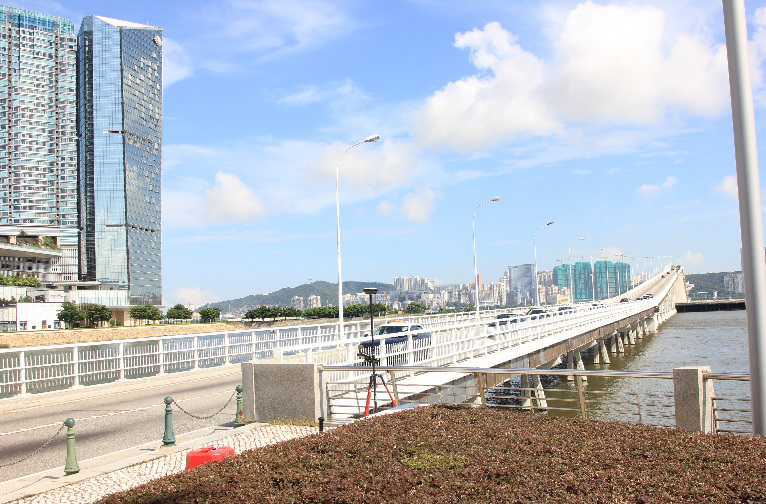
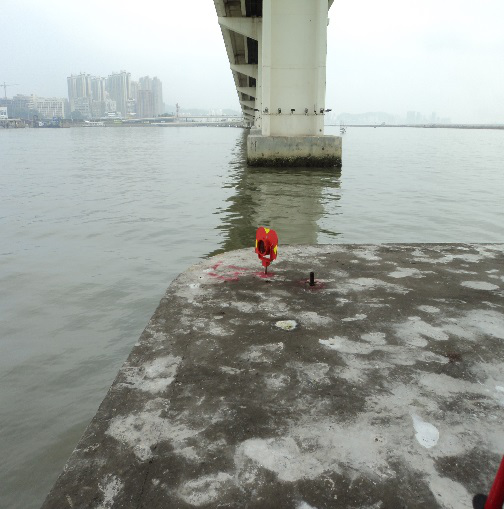
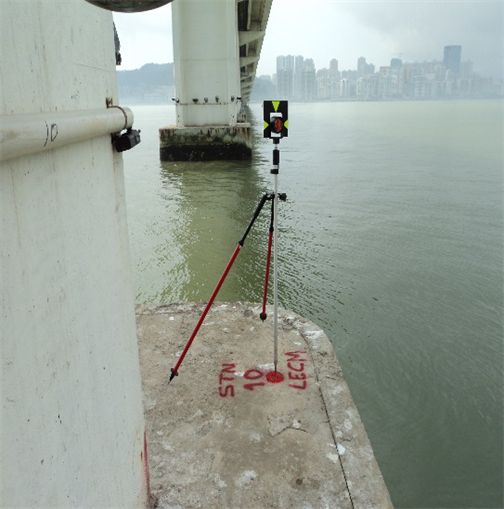





Nobre de Carvalho Bridge, Friendship Bridge and LECM – Civil Engineering Laboratory of Macau building under the rays of Total Station TM30 to measure any displacement.
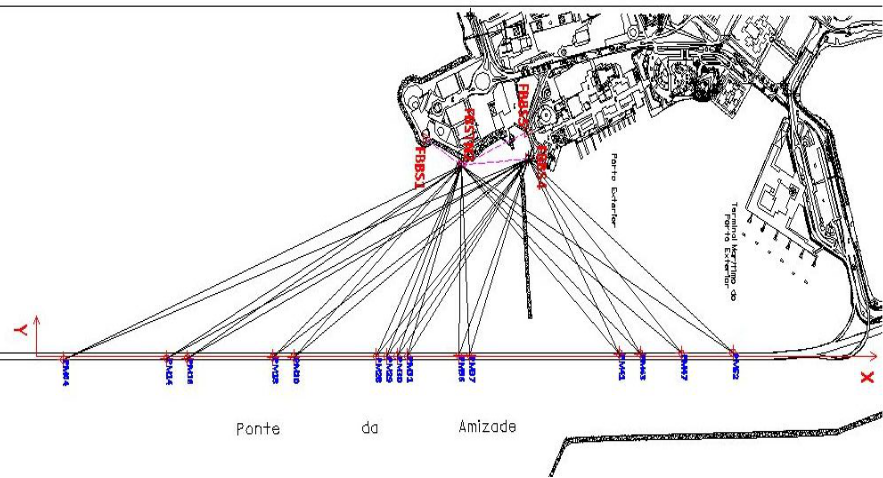
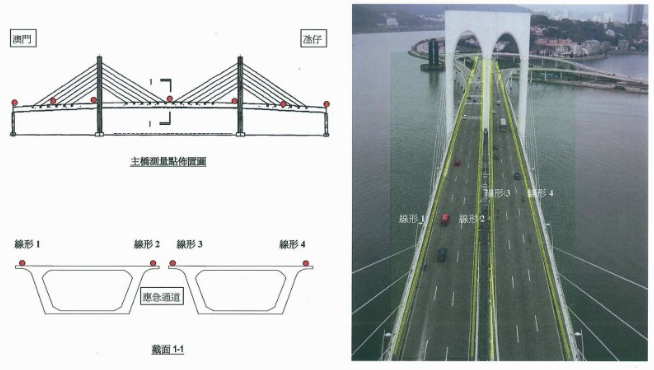
Location plan of survey points for Friendship Bridge Pile Caps. The reference and monitoring points are carefully selected and strategically located so as to be in line of sight and to ensure, stability and durability.
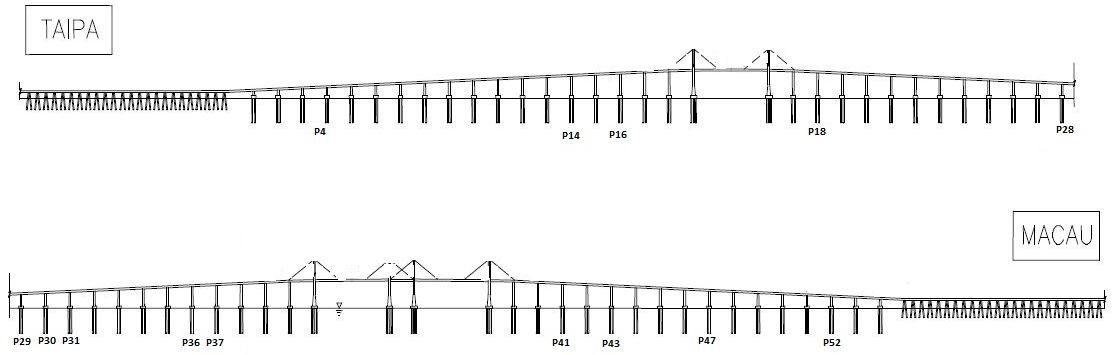
Profile of the Friendship Bridge showing the piers and deck under surveillance using Total Station Leica TM 30.
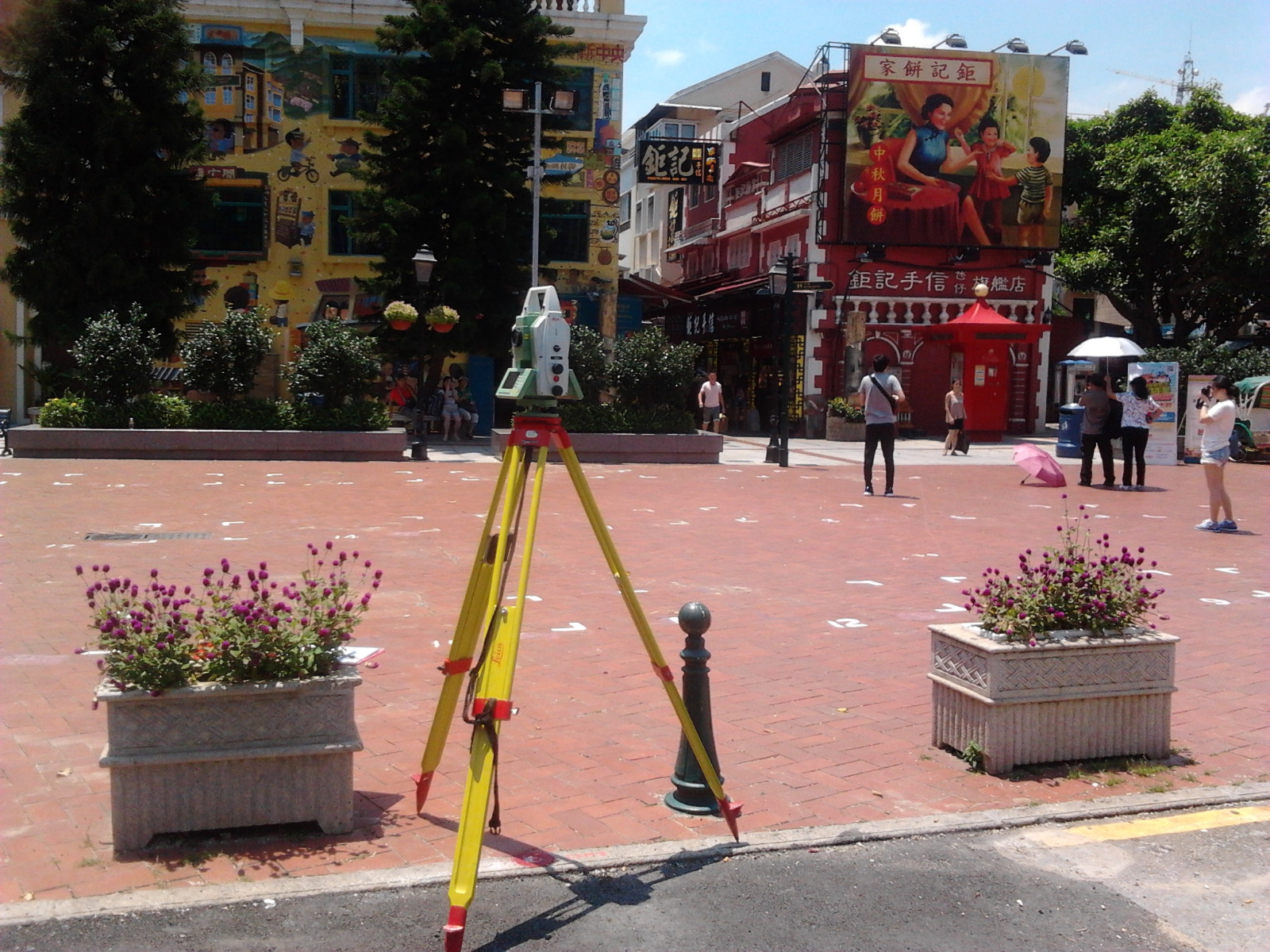

Old Taipa Village

Nobre de Cavalho Bridge

Ponte da Amizade

Nobre de Cavalho Bridge
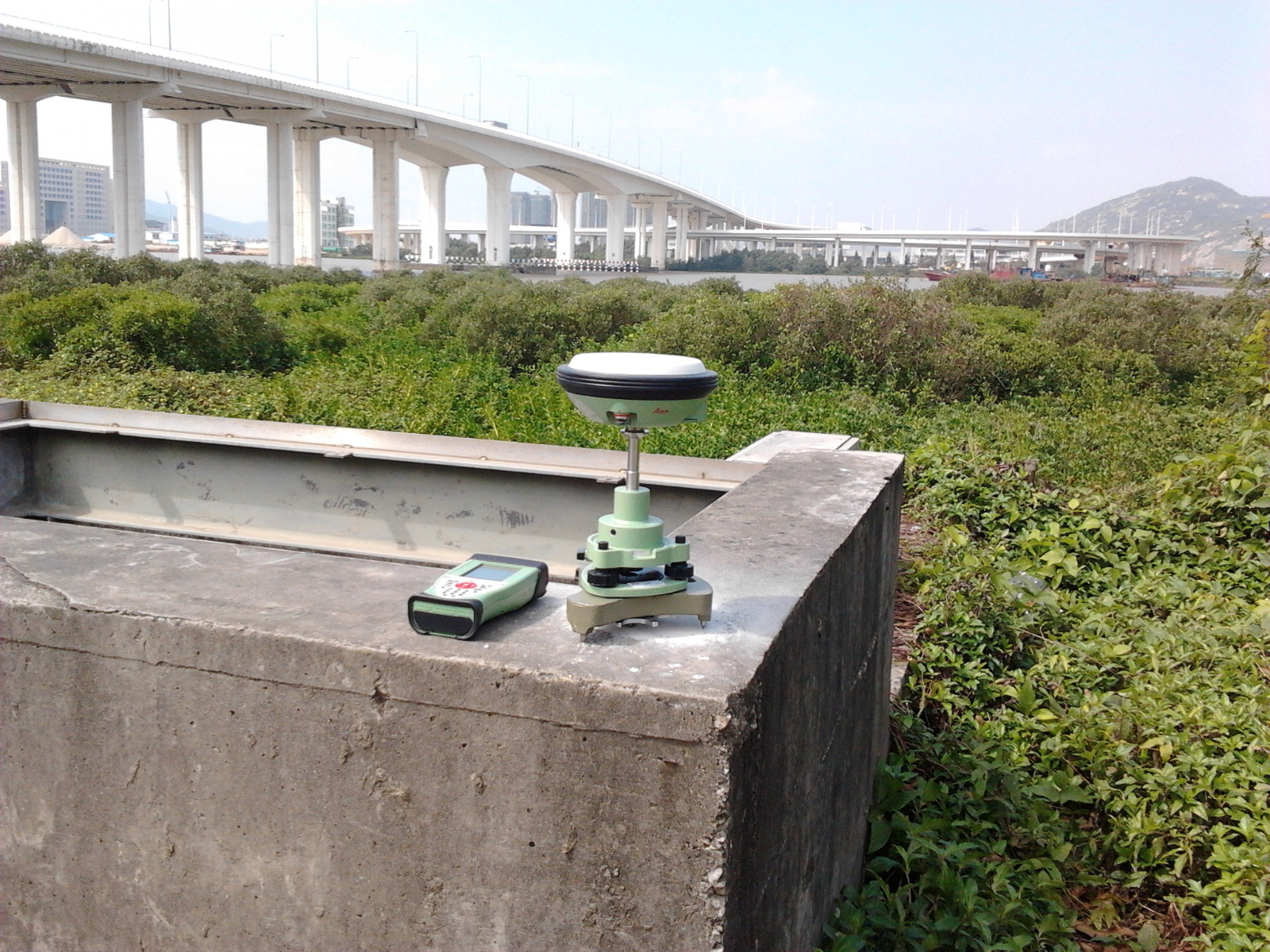
GNSS Surveying with LEICA GS14 + CS 10 /GS16 + CS 20 Measurement of Coordinates for Ground /Structures /Building
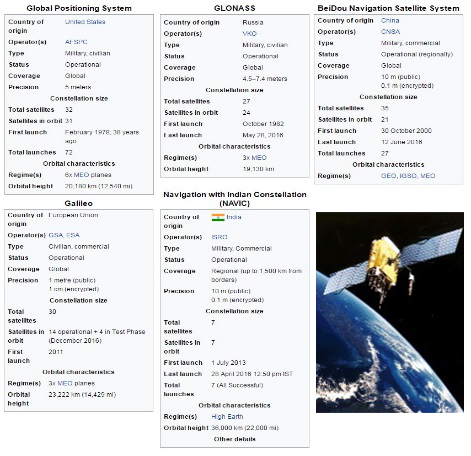
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) uses the satellite signals to provide positioning and timing data to measure the coordinates. Due to multiple satellites such as GPS: United States, GLONASS: Russia, BeiDou: China, Galileo: European and IRNSS: India, it effectively and intelligently adapts with the receiver on ground and selects the optimal signals to deliver the most accurate positions.
The reference station used are the CORS (Continuously Operating Reference Station) from the Macau Government -Direcção dos Serviços de Cartografia e Cadastro, installed in Macau (FOMO-2002), Taipa (DSMG-2008) and Coloane (COAL-2006).
GNSS acquires data at very high speed and provides real time coordinates and accuracy.The limitations faced with GNSS is that it requires open sky and is not well suited in crowded urban areas. It can provide an accuracy of 8-10mm (Horizontal) and 10-15mm (vertical)
Satellites in the orbit
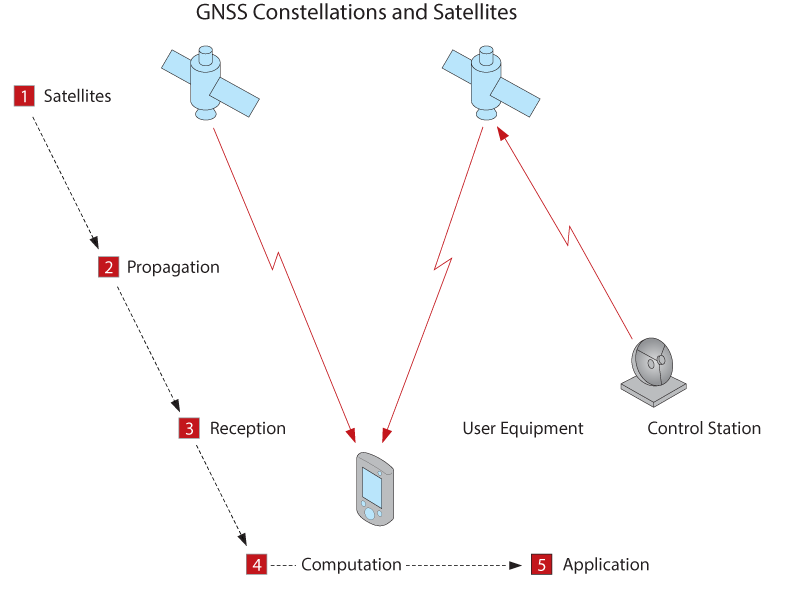
GNSS transmits the signals to the receiver and determines the positions
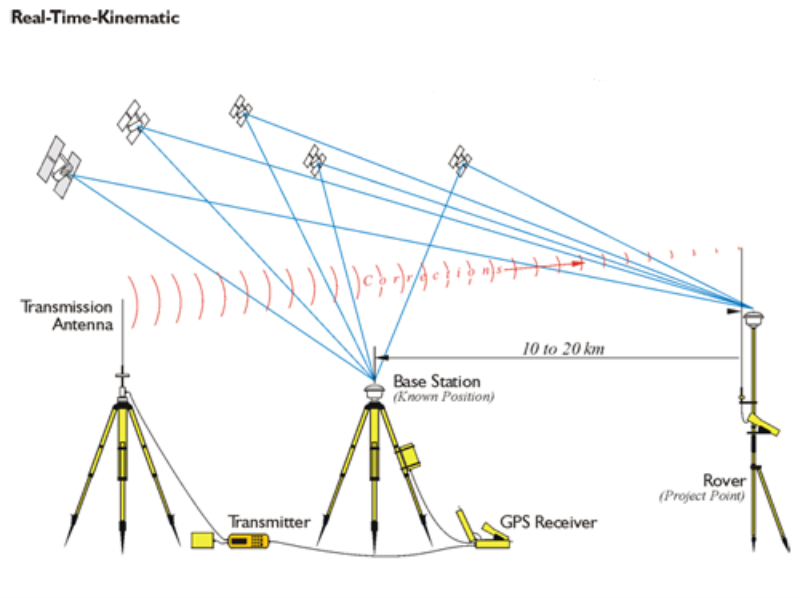
Signal Propagation from Satellite to receivers



DSCC’s CORS (Continuously Operating Reference Station

LECM’s receiver GS16 & GS14

Sai Van Bridge
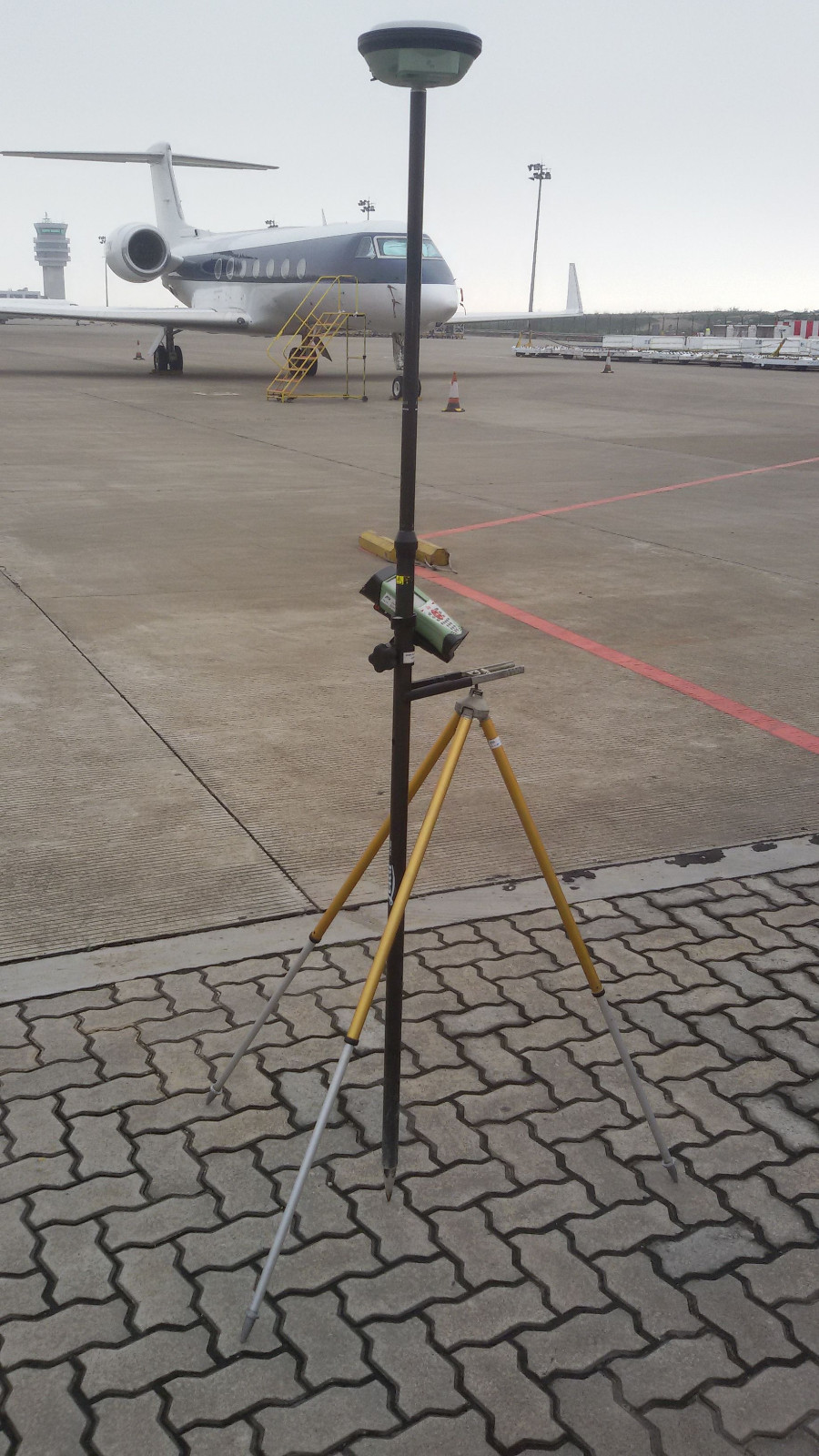

Macau International Airport - South Apron

Lotus Bridge
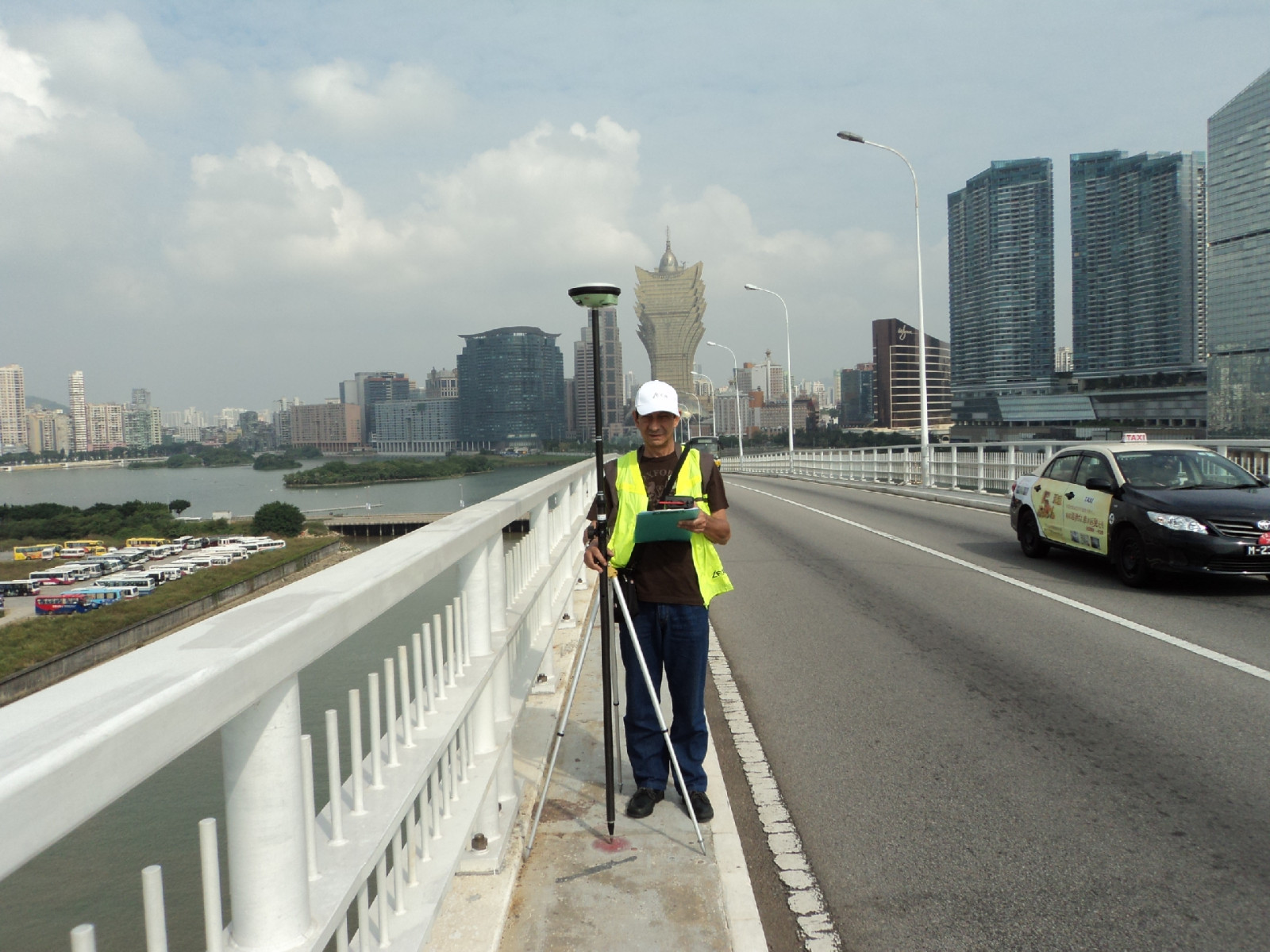

Nobre de Carvalho Bridge
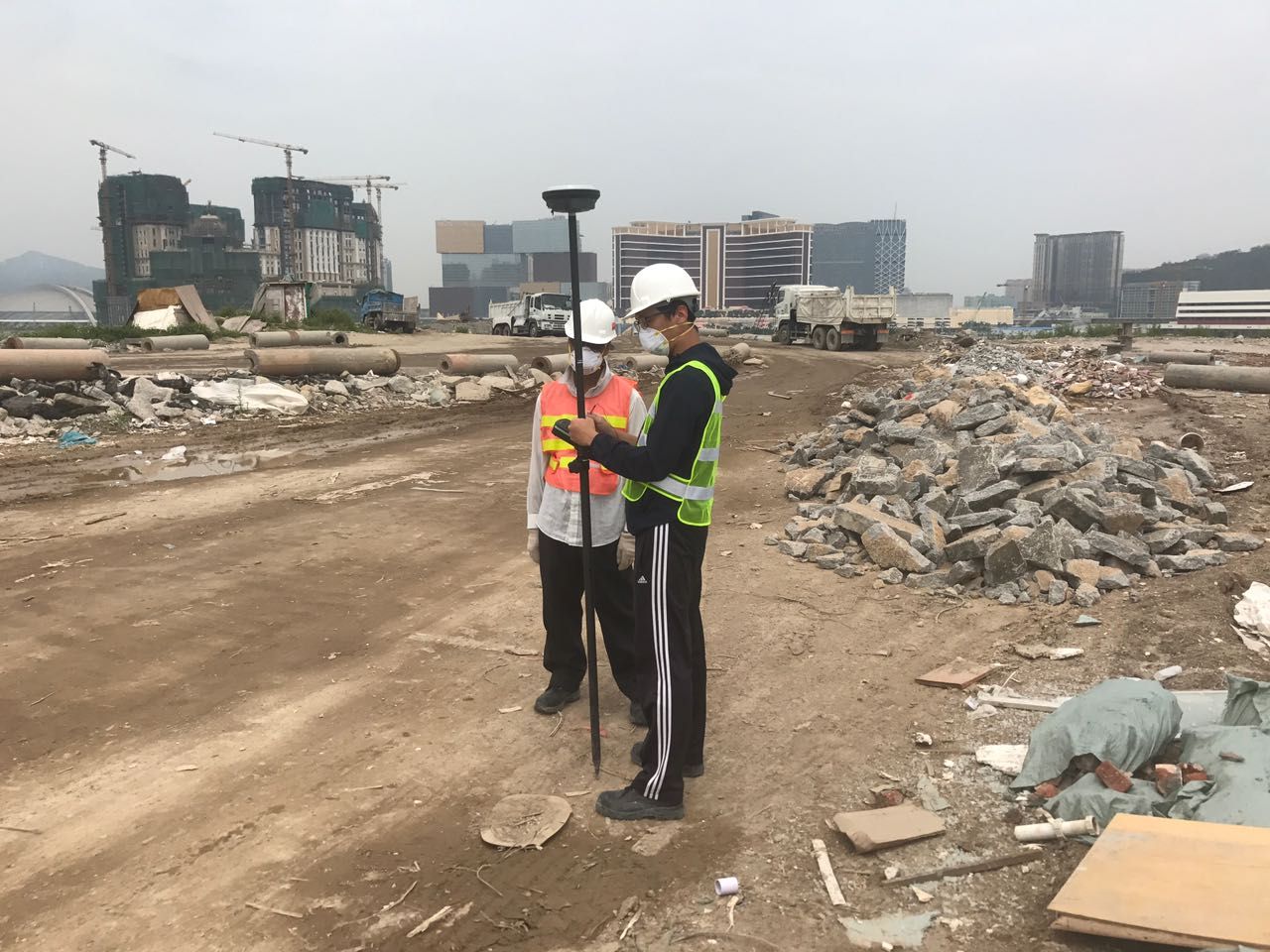

Construction Waste Land Fill
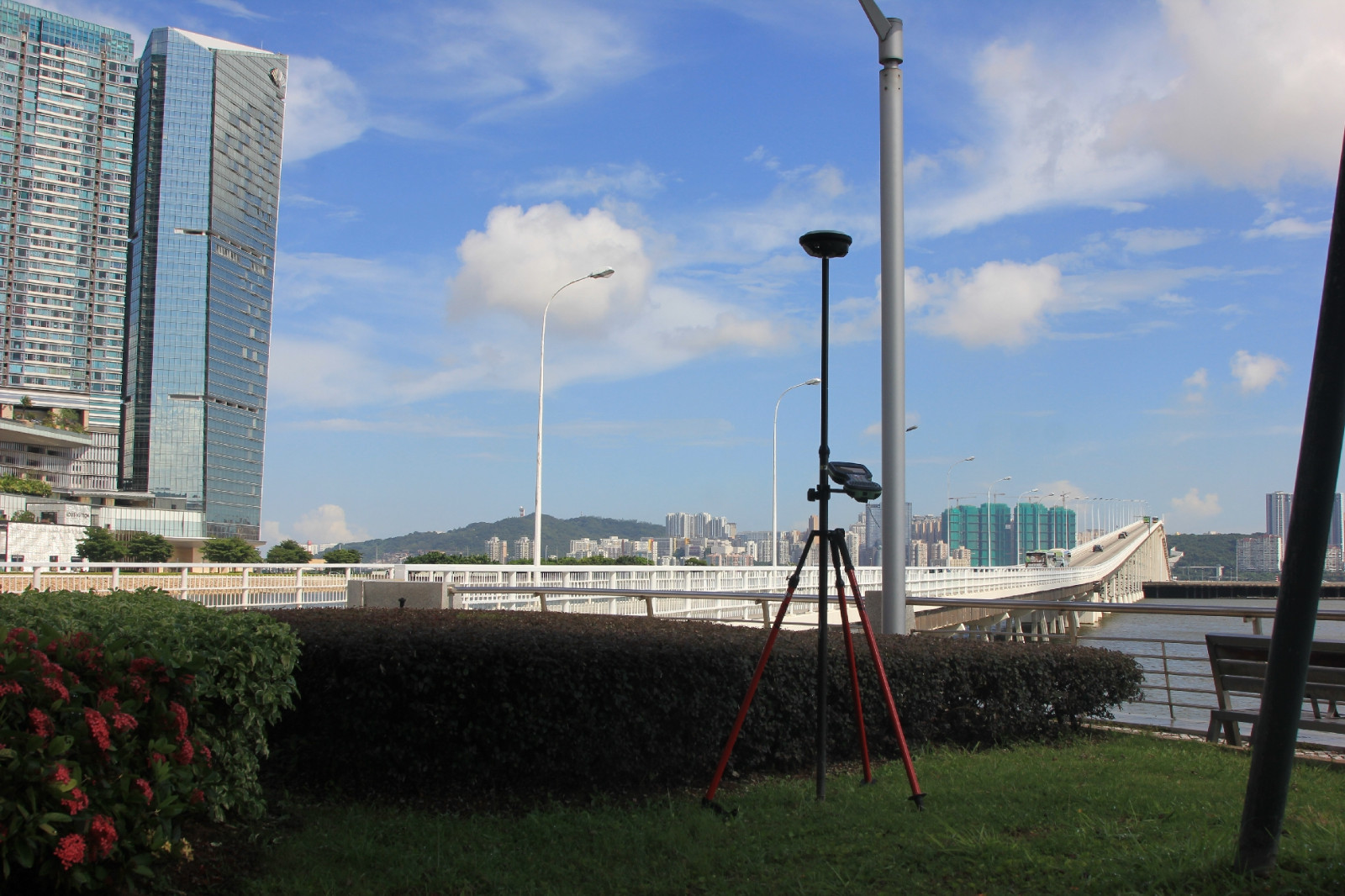

Nobre de Carvalho Bridge
Laser Scanning with LEICA ScanStation C10
Laser Scan is a state-of-the-art technology for scanning and photogrammetric coverage of any object. In the survey field is mainly used for scanning and photogrammetric coverage of slopes, terrains, structures like bridges, building façade, etc.
Laser scanning offers new capabilities in deformation monitoring, angle deviation etc. A laser scanner measures points in 3D by combining laser range finder and high accuracy angle measurements.
With laser scanning technology, LECM moved into the area of 3D modeling applied to civil engineering, namely, geometric monitoring and visual inspection.
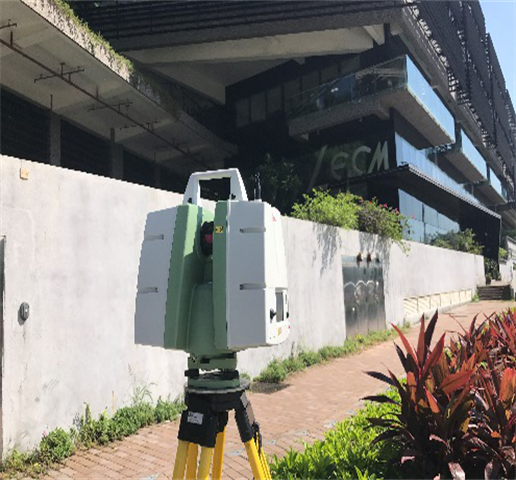

Laser scanner in operation for LECM building
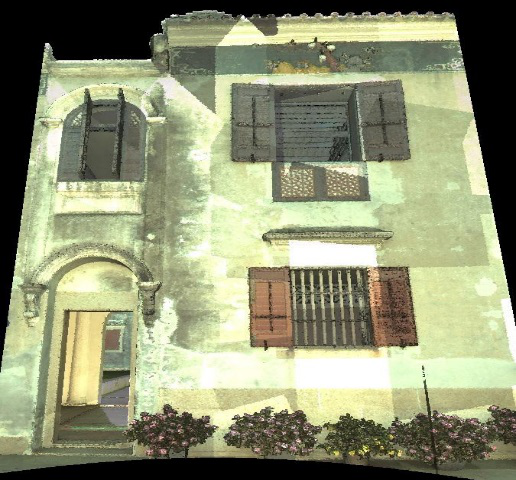

Example of an application to cultural heritage
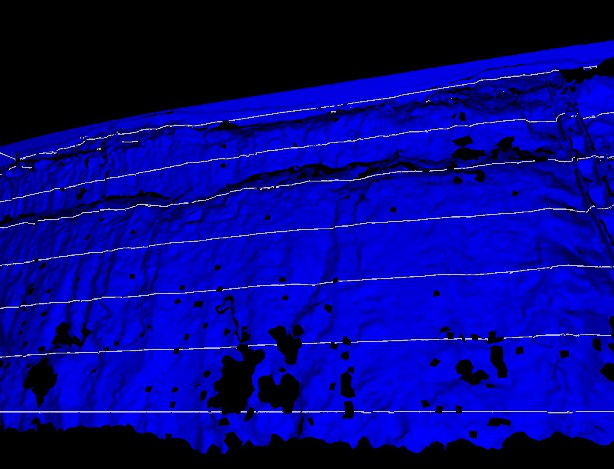
Synthesis of a slope 3D model by contour lines
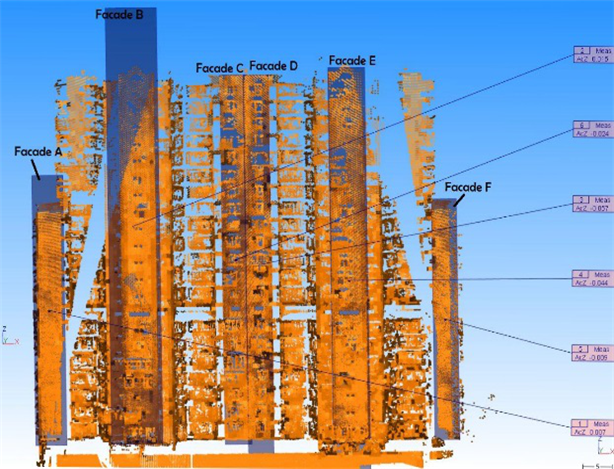
Measuring the inclination of large buildings
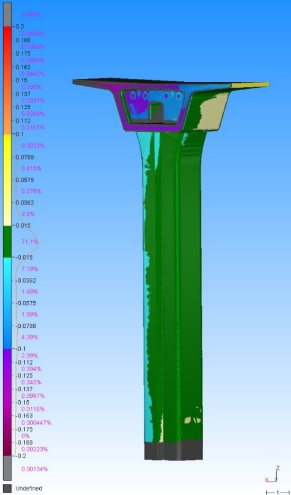
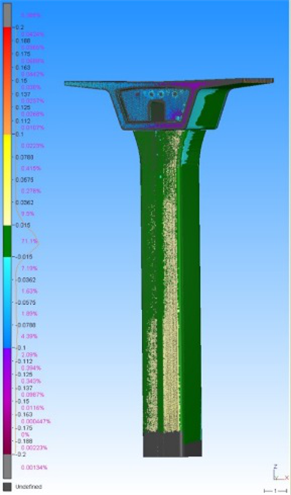
Comparison between design and as-built (LRT pillar)
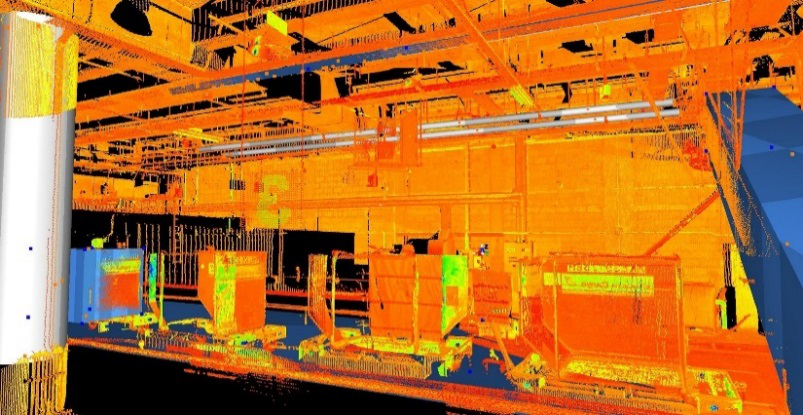
Point cloud of an area of the baggage handling area in the Macau International Airport

Macau Light Rail Transit

Macau Light Rail Transit

Nobre de Carvalho Bridge
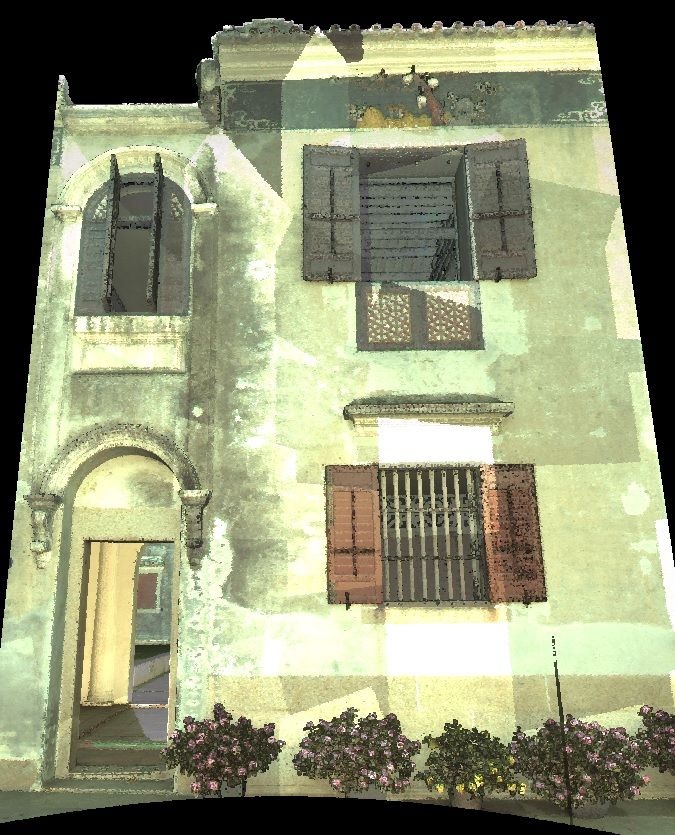

Mandarin's House


